Fiberglass Testing
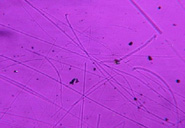
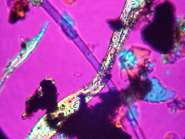
Fibrous Glass, Mineral Wool and Ceramic Fibers are covered in this test procedure. Analysis is performed by a combination of Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The data obtained by this combination can determine the presence of MMVF's and it can distinguish between the various forms. Many field personnel attempt to use Phase Contrast Microscopy (PCM) and the NIOSH 7400 fiber counting method for MMVF analysis, however, this test was not designed for this purpose and it is not even capable of identifying fibrous glass from other fibers.
In cases where MMVF's are suspected of causing Indoor Air Quality problems it is important to sample "Site Standards" for comparison to the MMVF's found in the area samples. By sampling questionable sources such as insulation, ceiling tiles and sound proofing, a forensic style of analysis can reveal the probable origin of the MMVF's isolated from the area samples.
When testing an area for MMVF's, it is important to sample the settled dust which represents the IAQ over an extended period of time. Furthermore, MMVF's tend to settle quickly and may not appear in air monitoring samples resulting in false conclusions. Settled dust and Site Standards can show the type, concentration and movement of the MMVF's throughout a building.
Various Test Types are as follows;
1) PCM -Test for total MMVF's and reports results as fibers per cc. This test will not positively ID MMVF's.
2) MMVF ID - This analysis will fully identify and quantitate all MMVF forms.
3) MMVF w/ Site Standards - This analysis is the same as the MMVF ID, however forensic comparison to bulk samples collected throughout the facility will be performed in order to identify the source of the problem.

 Order Sampling Supplies
Order Sampling Supplies Request Pricing
Request Pricing Technical Questions
Technical Questions 24/7 Account Access
24/7 Account Access Email Us
Email Us







